You cannot select more than 25 topics
Topics must start with a letter or number, can include dashes ('-') and can be up to 35 characters long.
9.2 KiB
9.2 KiB
| marp | paginate | math | theme | title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| true | true | mathjax | buutti | 4. RESTful HTTP Methods |
RESTful HTTP Methods
Contents
HTTP methods for RESTful APIs
RESTful API
- We'll be extending our Web API into a full-blown RESTful API
- It's a good idea to check out Webdev Basics: HTTP methods first
- Also, some ramblings about REST in Webdev Basics: REST Architecture
- We have so far implemented
GETandPOSTmethods for reading resources from the API and creating new ones to it, respectively - All the primary methods for following the uniform interface requirement are
GET,POST,PUT,PATCHandDELETE- Others exist, but these are by far most commonly used
- These methods correspond to CRUD operations Create, Read, Update and Delete
- CRUD describes what is done to a resource after a request is sent
Primary HTTP request methods
The primary HTTP request methods with descriptions:
| Method | Attribute | Description |
|---|---|---|
GET |
[HttpGet] |
Read a representation of a resource |
POST |
[HttpPost] |
Create new resources |
PUT |
[HttpPut] |
Fully update an existing resource |
PATCH |
[HttpPatch] |
Partially update an existing resource |
DELETE |
[HttpDelete] |
Delete a resource |
https://www.restapitutorial.com/lessons/httpmethods.html
HTTP POST method
Handling HttpPost Requests
- Remember that HTTP requests can include a content body
- In ASP.NET, this content is assigned to a variable with the
[FromBody]attribute:[HttpPost] public string[] Post([FromBody] string someContent) { // someContent holds the content of the request body return new string[] { text }; } - Note that the
[FromBody]attribute can only be used on one parameter - However, nothing prevents you from using a custom type variable
- ASP.NET deserializes the request content body into an object:
// Models/Contact.cs public class Contact { public int Id { get; set; } public string Name { get; set; } } -
// Controllers/ContactsController.cs [HttpPost] public Contact Put(int id, [FromBody] Contact contact) { // Contacts is a list of Contact objects, fetched from some repository Contacts.Add(contact); return contact; }
Creating a POST Request with Postman
Request headers
- ASP.NET knows to deserialize the content if the content type is set to JSON in the HTTP requests headers
- Headers are optional parameters that can be included in every HTTP request
- Headers are set in a Key-Value format
- When creating a request in Postman, to inform the server what type of content was just sent, add a new key
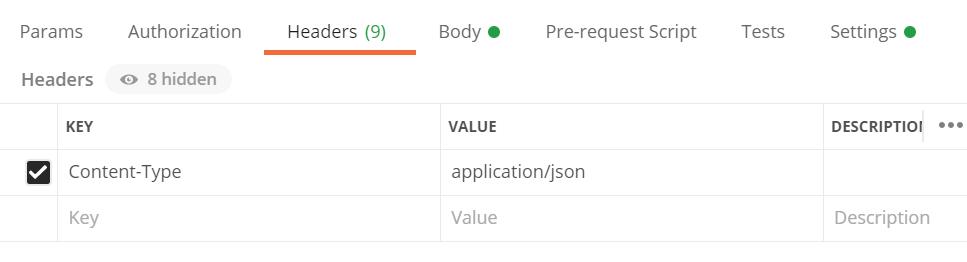
Content-Typeand set its value toapplication/jsonin the Headers tab:
Request body
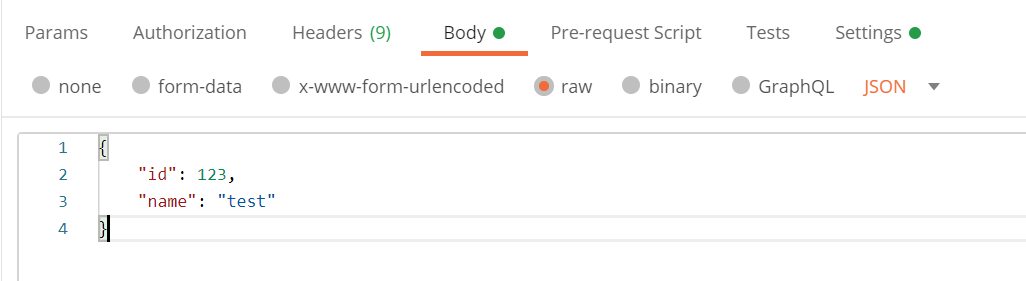
After setting the header,
- select the Body tab,
- change the content type to raw,
- select JSON from the dropdown menu, and
- insert the content in JSON format
Sending the request
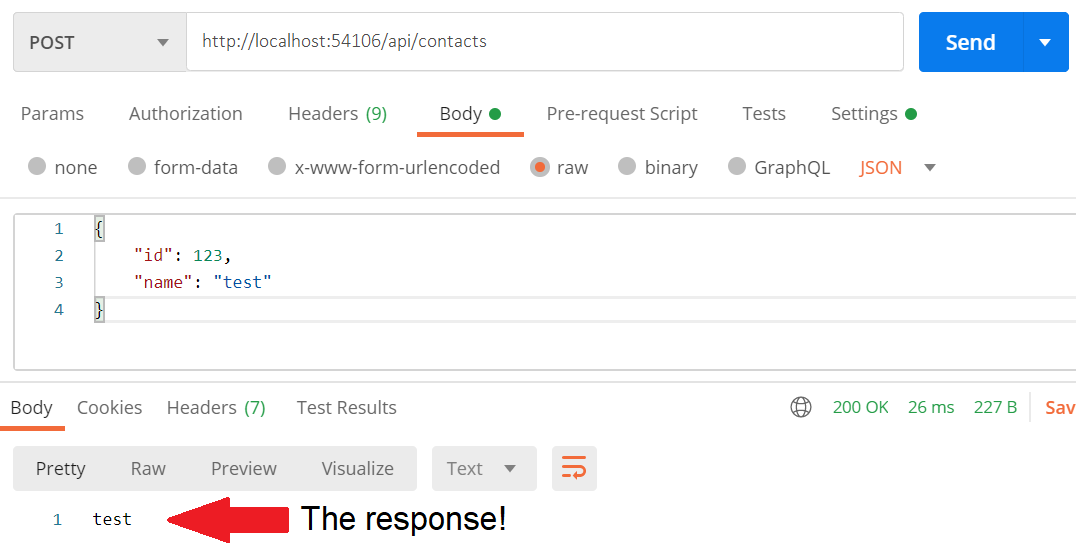
- If the
POSTmethod is routed athttp://localhost:54106/api/contacts:
Exercise 1: Creating a POST Endpoint
Continue working on the CourseAPI.
- Create a
POSTmethod and endpoint which adds a new course to the list in the repository with a running ID. Content and Author values are obtained from the request body: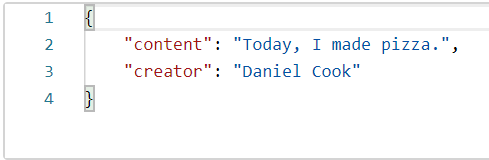
HTTP PUT method
- Use
PUTto replace an existing resource, e.g. an element in a list, with a new one - The ID of the resource to be replaced should be in the request URI
- The information about the new resource should be in the request body like in
POSTrequests
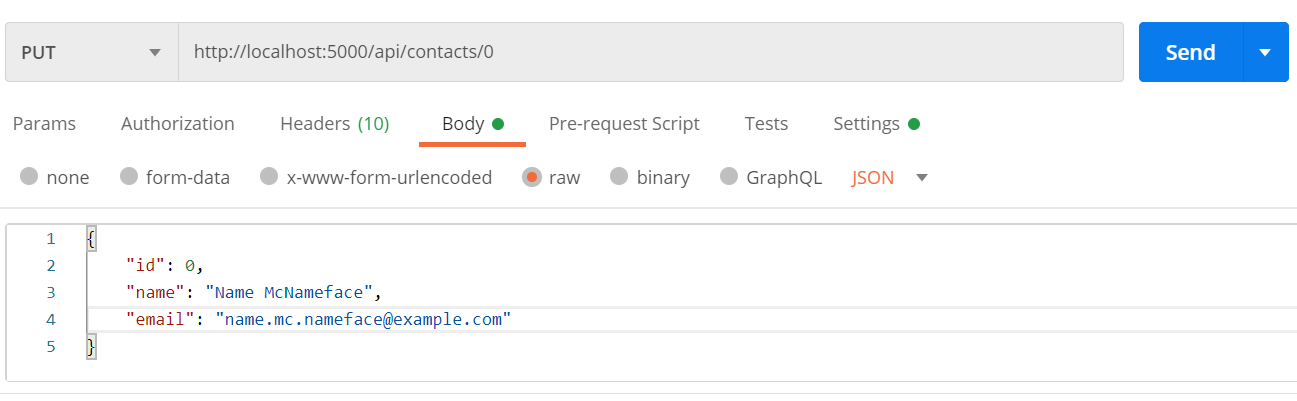
Handling HttpPut requests
- The ID is fetched from the URI and the contents from the request body
- Filtering is used to copy all objects from the original list except for the new
contactobject, which comes from body// Controllers/ContactsController.cs [HttpPut("{id}")] public List<Contact> Put(int id, [FromBody] Contact contact) { // Contacts is a list of Contact objects, fetched from some repository List<Contact> updatedList = Contacts.Select(c => c.Id != id ? c : contact).ToList(); Contacts = updatedList; return updatedList; }
Exercise 2: Creating a PUT Endpoint
- In CoursesController class, create a method for PUT requests with the URI api/courses/{id}
- The ID of the course to be replaced with should be in the request URI and the contents of the new course should be in the request body.
- The method should replace the corresponding course from the Courses list in the repository with the new course.
- The method should return the updated Courses list (for testing purposes)
- Return a 404 status code if a course with the corresponding ID does not exist
- Test with Swagger/Postman
HTTP DELETE method
- Use
DELETEto delete an existing resource, e.g. an element in a list - The ID of the resource to be deleted should be in the request URI
- As with the
GETmethod, a body is not needed
Handling HttpDelete Requests
- The ID is fetched from the URI
// Controllers/ContactsController.cs [HttpDelete("{id}")] public List<Contact> Delete(int id) { // Contacts = list of contact objects, fetched from some repository List<Contact> updatedList = Contacts.Where(c => c.Id != id).ToList(); Contacts = updatedList; return Contacts; }
Exercise 3: Creating a DELETE Endpoint
Continue working on CourseAPI.
- Create an endpoint for
DELETErequests with the URIapi/courses/{id}a) The ID of the course should be fetched from the URI b) The corresponding course should be removed from the list of courses in the repository c) The method should return the updatedCourseslist (for testing purposes) d) Return a404status code if a course with the corresponding ID does not exist - Test with Postman.
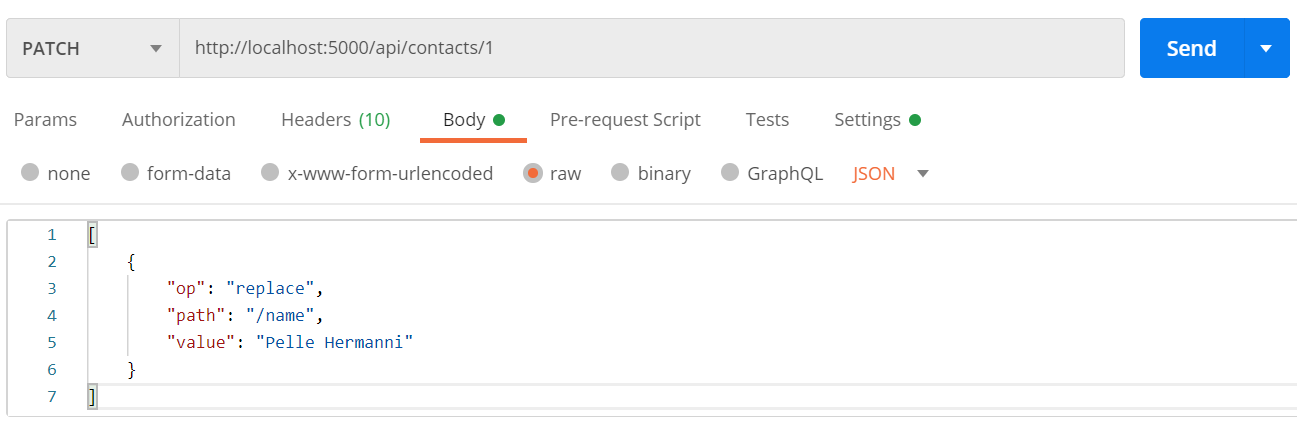
HTTP PATCH method
- Use
PATCHto partially update a resource- I.e., update some value inside of a resource
- This saves some resources as only a part of a resource has to be sent instead of an entire document (as opposed to
PUTrequests)
- Sending and handling
PATCHrequests with ASP.NET requires some extra work and the use of a third party package JSON Patch
- To handle
PATCHrequests in a standardized way, install and add the following NuGet packages to your project:Microsoft.AspNetCore.JsonPatchMicrosoft.AspNetCore.Mvc.NewtonsoftJson
- Then, change the following line in
Program.cs:builder.Services.AddControllers(); - to this:
builder.Services.AddControllers().AddNewtonsoftJson();
- The body of the
PATCHrequest needs to be in the following form:[{ "op": "replace", "path": "/propertyName", "value": "newValue"}] - Use the URI to specify the ID of the resource to update
Handling HttpPatch Requests
- The ID is fetched from the URI
- The property and its new value are specified in the body, which is retrieved as a
JsonPatchDocument PATCHis operated on the targeted object:// Controllers/ContactsController.cs [HttpPatch("{id}")] public List<Contact> Patch(int id, [FromBody] JsonPatchDocument<Contact> patchDocument) { // Contacts is a list of contact objects, fetched from some repository var contact = Contacts.FirstOrDefault(c => c.Id == id); if(contact != null) { patchDocument.ApplyTo(contact); } return Contacts; }
Exercise 4: Creating a PATCH Endpoint
Continue working on CourseAPI.
- Create an endpoint for PATCH requests with the URI
api/courses/{id}a) The ID of the course should be fetched from the URI b) The corresponding course should be updated according to the JSON PATCH document in the request body c) The method should return the updatedCourseslist (again, for testing purposes) d) Return a404status code if a course with the corresponding ID does not exist - Test with Swagger/Postman. Try to change the number of credits for some course!