You cannot select more than 25 topics
Topics must start with a letter or number, can include dashes ('-') and can be up to 35 characters long.
7.0 KiB
7.0 KiB
| marp | paginate | math | theme | title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| true | true | mathjax | buutti | 1. Introduction to the Web |
Introduction to the Web
Contents
- Web and the Internet
- Frontend and backend
- Anatomy of a website
- Web APIs
Web and the Internet
What is the Internet?
- World Wide Web is not the Internet
- Internet: connected networks that use the TCP/IP protocol
- made out of billions of computers, cables and antennae directing data to the right direction
- World Wide Web: URL-based information system
- Internet: connected networks that use the TCP/IP protocol
- WWW is a big part of the Internet but it consists of other kinds of traffic, too:
- VoIP (Skype, Discord, etc)
- File transfer between computers (FTP)
- remote connections to other computers
- In other words, the Internet is an infrastructure and WWW is served via it
What is the Web?
- World wide web (www) is the part of the Internet where browsers fetch and show websites
- WWW makes sites and applications accessible to all kinds of devices:
- mobile phones, computers, smart watches, TVs...
- For the websites to appear on all the different devices similarly, strict rules are needed
Frontend vs Backend
- Web development is split into frontend and backend
- Frontend is the website users can actually see
- Visual elements of a website or app the user can interact with
- Backend is the invisible part
- "Server side" where user's data is stored
- Backend is not interacted with directly, but gives and modifies its stored data based on user requests
- Full stack development refers to working on both backend and frontend!
What is a server or "the cloud"
- A server or "the cloud" is just another computer, or multiple ones
- Server software is constantly running on it
- Your own computer could be a server!
- If you need to save an image, post a comment on a news website, or just load a website, you send a request to a server
- Server then gives an appropriate response based on the request
Backend
- Backend handles e.g.,
- saving and fetching user data from a database
- user authentication and connecting multiple users together (chat apps!)
- Databases are used with query languages like SQL
- Backend software can be written with various different programming languages
- even with JavaScript! See: Express
- Simple websites don't require a dedicated backend
Anatomy of a website
Building blocks of a website
- Historically, websites looked something like this
- Nowadays, a website can even be a full-blown application!
- Old and new sites alike are written in HTML, which describes the structure of the site
- In mid-90s, plain HTML was extended with CSS to implement styling
- The third building block of a website is JavaScript, or JS, which is used to add interactivity
HTML
- HTML stands for Hypertext markup language
- HTML defines the structure of a website
- It tells what text, images and containers the website has
- You might have seen raw html if your browser has failed due to a slow connection
\Rightarrow - motherfuckingwebsite.com
- http://catb.org/~esr/open-source.html
<body>
<h1>This is a Heading</h1>
<p>This is a paragraph.</p>
</body>
CSS
- CSS stands for Cascading style sheets
- CSS defines the look of the website
- It tells the fonts, sizes, colors and locations of elements
- Can be used to animate elements
body {
background-color: lightblue;
}
h1 {
color: white;
text-align: center;
}
p {
font-family: verdana;
}
JavaScript
- With a dedicated programming language, JavaScript, your website can become interactive
- It allows you to add functionality to buttons, send data to / fetch data from a server in real time
Web APIs
What is a Web API
- API (Application Programming Interface) defines a way of communicating between applications
- A Web API defines how a client can communicate with a web server
- With the help of APIs, you don't need to create all functionality yourself
- Each program that wants to communicate to the outside world defines their own interface
- There are some architectural models like REST (Representational State Transfer) that exist to generalize API design
Client-side and Server-side APIs
- Client-side APIs — called on the web browser (client side):
- Browser APIs, built into the browser itself and extend its functionality
- For instance, the geolocation API returns coordinates where the browser is located
- Third-party APIs, for retrieving data from somewhere on the Web
- Browser APIs, built into the browser itself and extend its functionality
- Server-side APIs — called on the server:
- For communicating between servers or the client
- Consist of multiple exposed endpoints with a defined request-response system
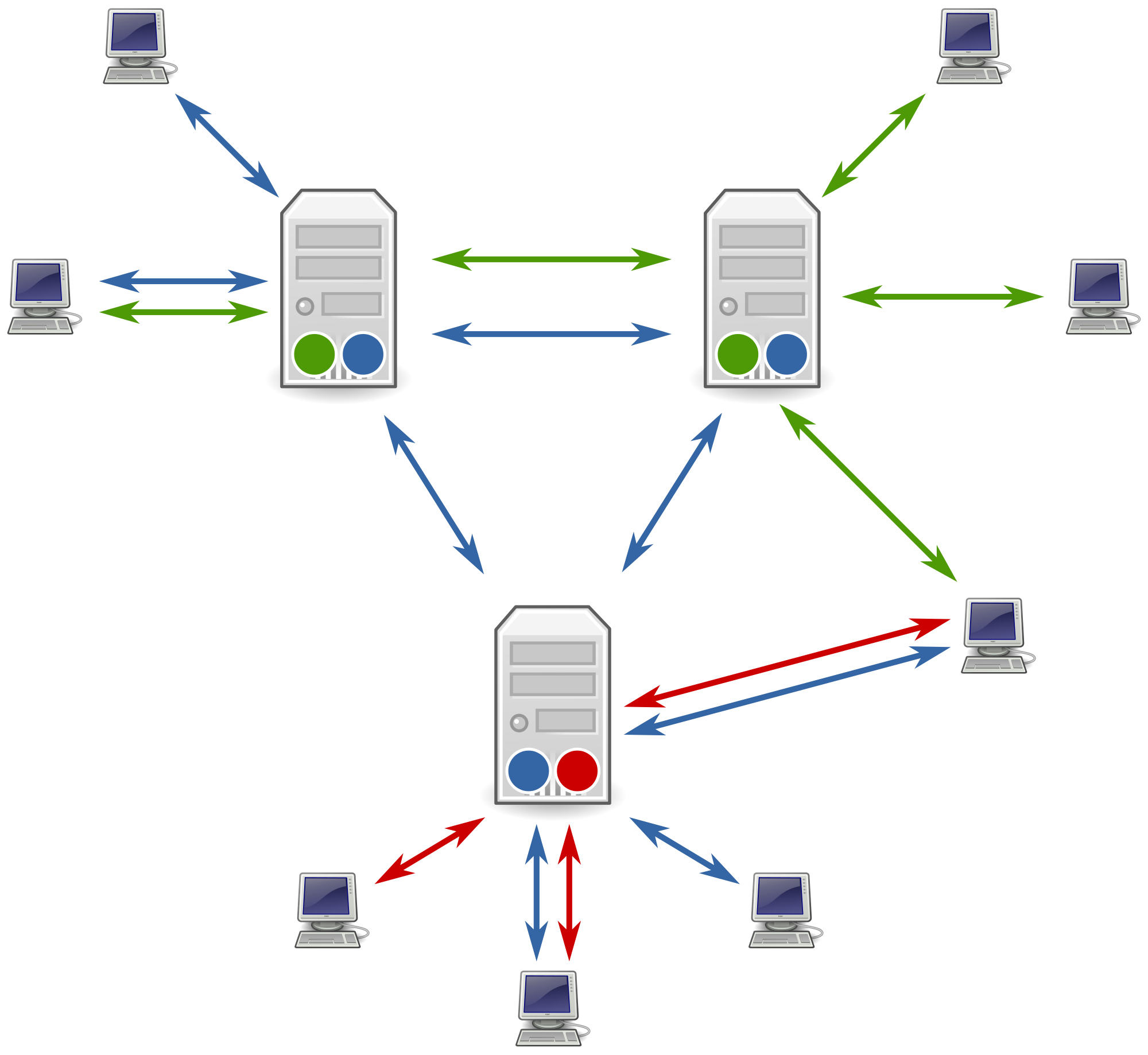
API communication
Third party APIs
- Many services have public APIs that anyone can use
- Some services require users to have an API key