You cannot select more than 25 topics
Topics must start with a letter or number, can include dashes ('-') and can be up to 35 characters long.
4.8 KiB
4.8 KiB
| title | marp | paginate | theme |
|---|---|---|---|
| Project management 0. Git setup | true | true | buutti |
Project management 0. Git setup
Contents
- Contents
- What is Git?
- GitHub and other developer platforms
- Setup
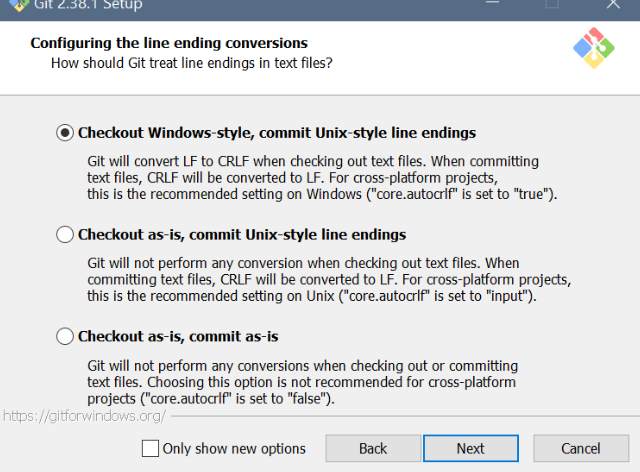
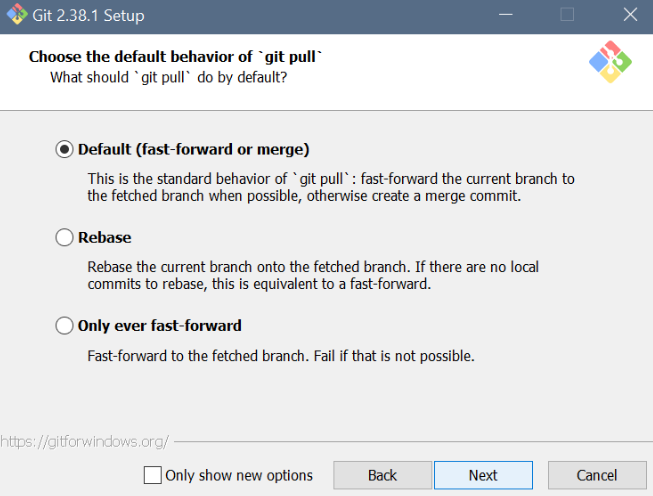
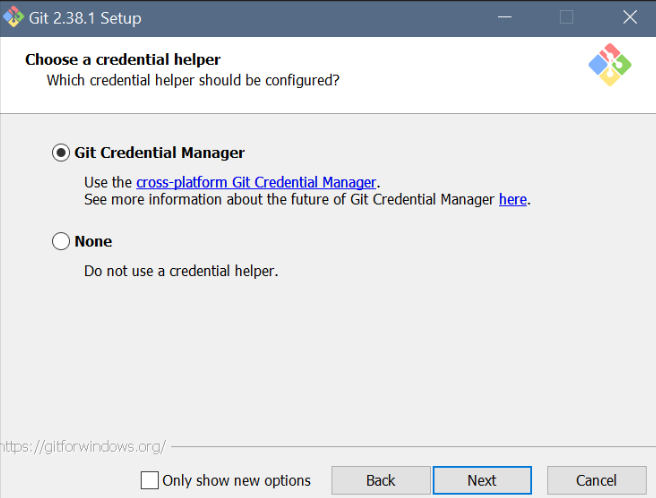
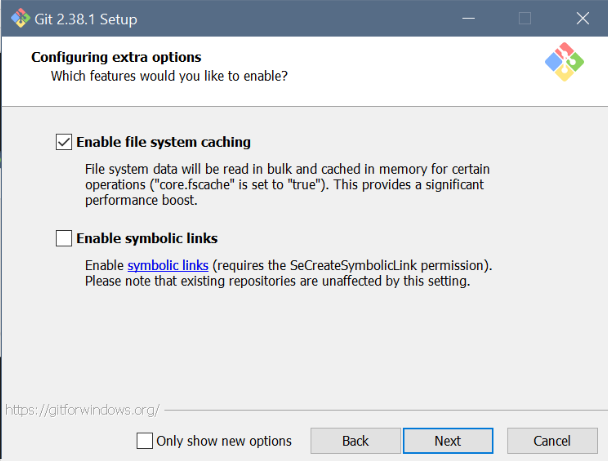
- Git setup: Settings for Windows
- Command line
- Extra: Help, this is horrible!
- Btw: Config
What is Git?
- Git is a version control tool originally created by Linus Torvalds in 2005
- Keeps track of code changes
- Can be used to backup code in the cloud
- Enables cooperation with other team members
- Ubiquitous in software development
Git vs cloud storage
- Git is different from cloud storage services like Dropbox, Google Drive or OneDrive
- Instead of automatic syncing, you deliberately push to and pull from the cloud
- Cloud services are easier for starters
- ...but in projects of more than one person, tracking changes would be a pain
- Git has a steep learning curve
- To ease things, there are some visual tools like Sourcetree or Sublime Merge
- To use them effectively, you still need to understand how Git works, though
GitHub and other developer platforms
- Git could be used locally, but its usage is almost always combined with a developer platform — a remote storage service like GitHub, GitLab or BitBucket
- These services can also double as a programming portfolio
- Commonly used in both open source and commercial projects
- In Buutti's trainings, GitLab is most commonly used
Setup
- Install Git
- Windows/Mac: git-scm.com
- Installation instructions are included in the following slides.
- If a setting is not mentioned in the instructions, you can leave it as the default option.
- Linux:
sudo apt-get install git
- Windows/Mac: git-scm.com
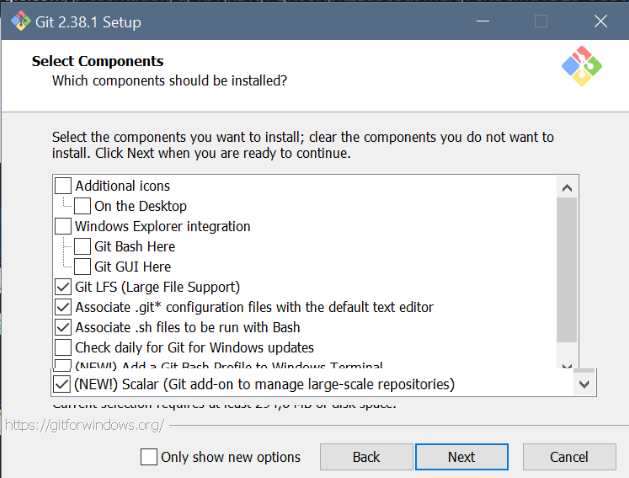
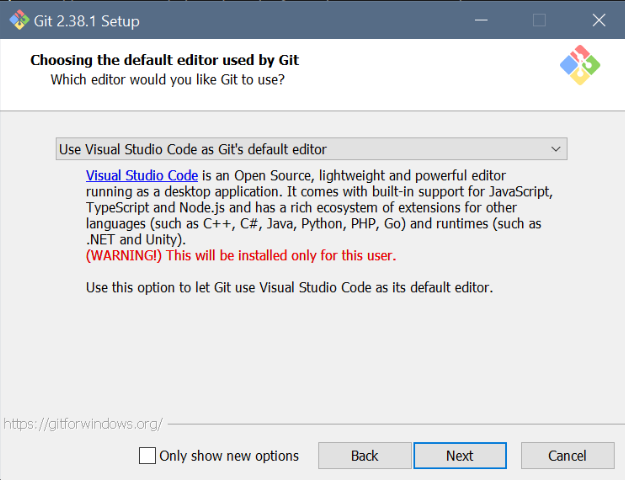
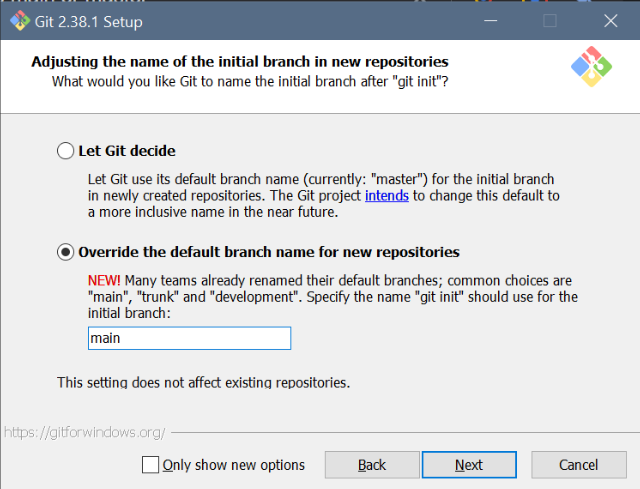
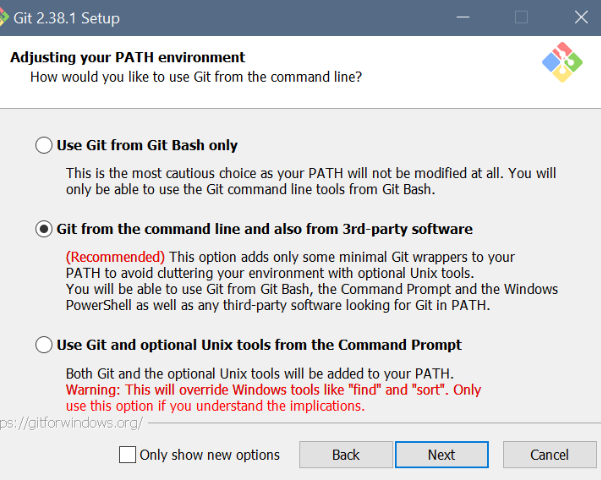
Git setup: Settings for Windows
Command line
- Git is operated via the command line, a.k.a, the terminal
- There are many kinds of command line syntaxes out there. Some examples:
- Windows: PowerShell (new), cmd (old)
- Linux, (also included in the Windows Git install): bash
- We're using PowerShell, which can be accessed inside VS Code
- In VS Code, open/close terminal by pressing CTRL+Ö (in the Fin/Swe layout)
Basic commands and the working directory
- To do actions in Git, you don't press buttons, you write commands
- Most commands act on the currently open folder, a.k.a. the working directory
- Path to the directory is shown next to the terminal cursor:
PS E:\borb\code\unity-basics-course>
- Path to the directory is shown next to the terminal cursor:
lstells the contents of the working directorycdis used to move to another directory- Use
cd programmingto move to theprogrammingsubfolderPS E:\borb\code\unity-basics-course\programming> - Use
cd ..to move one step up in the hierarchy (to the parent directory)PS E:\borb\code\unity-basics-course>
- Use
- Note:
..is a shorthand for to the parent directory,.for the current directory
Extra: Help, this is horrible!
- Do you feel more at home in graphical UIs?
- There are also graphical user interfaces for Git like GitKraken, Sublime Merge or GitHub Desktop (GitHub only)
- VS Code also has very useful graphical tools for Git (more about them later!)
- However, the GUIs make a lot more sense after you've understood the Git commands that those GUIs still execute under the hood
- There is no free lunch here
Btw: Config
- To configure your Git username for every project:
- Use
git config --global user.name "myUserName" - and
git config --global user.email "my.email.address@domain.com"
- Use
- If you do not do this, Git will ask to do it anyway at some point