3.6 KiB
Loops
Overview
While Loop
For Loop
Nested Loops
Breaking Out of Loops
Loops
Loops are useful when you need to repeat a block of code multiple times and to avoid code like this:
Console.WriteLine(count);
++count;
Console.WriteLine(count);
++count;
Console.WriteLine(count);
// Yuck! Nobody wants to see this.
Loops can also be used for iterating through arrays and lists (more on those later)
while Loop
while loop keeps executing its code block as long as the condition in its statement is true:
int count = 0;
while(count < 4)
{
Console.WriteLine(count);
++count;
}
// Outputs '0', '1', '2' and '3'
do..while Loop
do..while works the same way as while, but it executes the code at least once and checks the condition at the end:
int count = 0;
do
{
Console.WriteLine(count);
++count;
} while (count < 4);
// Outputs '0', '1', '2' and '3'
for Loop
_for _ loops are used when the number of iterations are predefined
for loop executes in three inherent steps:
for (/initial value/;/condition/;/increment/)
{
/* Code to be executed */
}
The initial value is set before the first iteration. The condition is checked before each iteration, and the increment is executed after each iteration.
for Loop (continued)
Try to understand the following two examples:
for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i)
{
Console.WriteLine
("Current: " + i);
}
/* Outputs
Current: 0
Current: 1
Current: 2
Current: 3
*/
for (int i = 8; i > 0; i -= 2)
{
Console.WriteLine
("Current: " + i);
}
/* Outputs
Current: 8
Current: 6
Current: 4
Current: 2
*/
We start from zero, print the current value and add one until the value is no longer under four.
We start from eight, print the current value and remove two until the value is no longer larger than zero.
for (int i = 8; i > 0; i -= 2)
{
Console.WriteLine
("Current: " + i);
}
for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i)
{
Console.WriteLine
("Current: " + i);
}
Nested Loops
Nothing prevents you from using a loop inside another loop:
int columns = 3;
int rows = 4;
for (int i = 0; i < columns; ++i)
{
for (int j = 0; j < rows; ++j)
{
// Console.Write doesn't add a line break after printout
Console.Write("(" + j.ToString() + "," + i.ToString() + ")");
}
Console.WriteLine("");
}
Breaking Out of Loops
To stop the execution of a loop completely, use the _break _ -keyword:
int i = 0;
while(true)
{
++i;
if(i > 3)
break;
}
// i is now 4
To skip the current iteration, use the _continue _ -keyword
int i = 0;
while(i < 10)
{
++i;
if (i % 2 == 0)
continue;
Console.WriteLine(i);
}
// Prints every odd number from 1 to 10
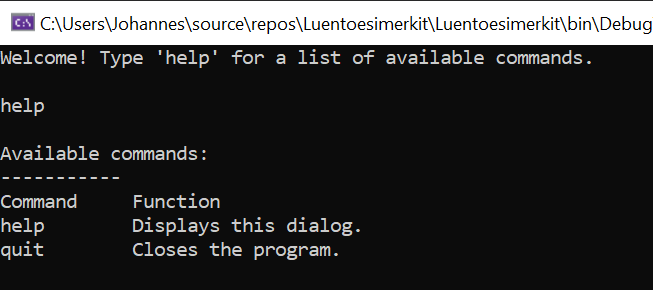
Exercise 1: The Main Loop
At the heart of every dynamic program, there is something called the _event loop _ a.k.a the _main loop. _ Create a console application which keeps asking the user for an input, until the user inputs "quit".
Expand the program so that if the user inputs "help", a dialog shows up which shows the command and explanation for the command for both quit and help commands.
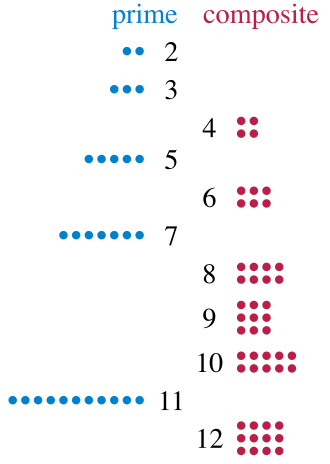
Exercise 2: Prime Numbers
Prime number is a number greater than 1 that is not a product of two small numbers, i.e. cannot be divided into a whole number. (Wikipedia: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Prime_number )
Create a console application which prints all the prime numbers between 0 .. 40