You cannot select more than 25 topics
Topics must start with a letter or number, can include dashes ('-') and can be up to 35 characters long.
4.6 KiB
4.6 KiB
| marp | paginate | math | theme | title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| true | true | mathjax | buutti | 5. Model Validation & API Design |
Model Validation & API Design
Model validation in ASP.NET
- ASP.NET has a built-in system for validating whether the data sent in requests fits the model set in the code
- Additional requirements can be set with attributes
public class Contact { public int Id { get; set; } [Required] [MaxLength(50)] public string Name { get; set; } [MaxLength(100)] public string Email { get; set; } }
TryValidateModel
- An object can be validated at any time with
TryValidateModelmethod:[HttpPost] public IActionResult Post([FromBody] Contact contact) { if (!TryValidateModel(contact)) { return BadRequest(ModelState); } Contacts.Add(contact); return Created(Request.Path, contact); }
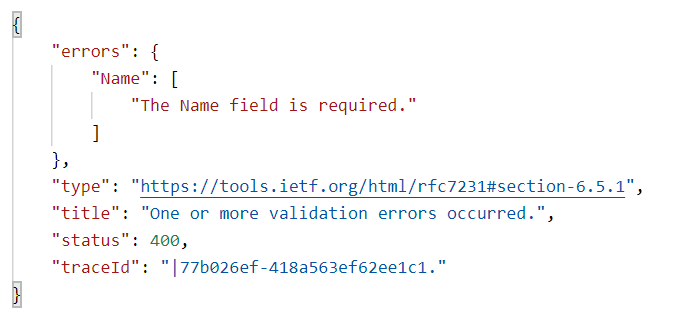
- The attributes set a corresponding error message and information to the
ModelStatewhich is sent with the bad request result
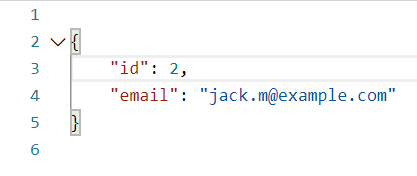
- Sometimes you might have custom requirements and the action should, according to the standard, return a bad request if the action does not fit those requirements
- For example, the simplest possible way to validate the format of an email is to check whether it contains the
@symbol- Add an error with
AddModelErrorif it does not contain the symbol:if (!contact.Email.Contains('@')) { ModelState.AddModelError("Description", "The email is not in valid form."); } - Then check the model state:
if (!ModelState.IsValid) { return BadRequest(ModelState); }
- Add an error with
Exercise 1: Add validation
Continue working on CourseAPI.
- Mark all the properties of the Course class with the
[Required]attribute - Create an endpoint for
POSTrequests with the URIapi/courses - All the contents of the new course should come from the request body and the new course should be added to the
Courseslist - The maximum number of credits should be 20 and minimum 1 (Tip: Use
Range) - Return an appropriate response
Limiting PATCH with validation
- Suppose we only want to allow the
PATCHoperation to affectNameandEmailproperties of theContactclass - Begin by declaring a class with only those fields:
// Models/ContactPatch.cs public class ContactPatch { public string Name { get; set; } public string Email { get; set; } }
- Use the
ContactPatchclass instead of the actual class for patching:// Controllers/ContactsController.cs [HttpPatch("{id}")] public IActionResult Patch(int id, [FromBody] JsonPatchDocument<ContactPatch> patchDocument) { Contact initialContact = _contactRepository.GetContact(id); ContactPatch patchContact = new ContactPatch { Name = initialContact.Name, Email = initialContact.Email }; patchDocument.ApplyTo(patchContact, ModelState); if (!ModelState.IsValid) { return BadRequest(); } initialContact.Name = patchContact.Name; initialContact.Email = patchContact.Email; _contactRepository.UpdateContact(id, initialContact); return Ok(initialContact); }
Designing APIs
- It can be useful to sketch an overview of the API before starting to implement it.
- Write a table with all the endpoints, writing out the
- HTTP method
- Description of the method
- HTTP code on success
- HTTP codes on different failure states
- See the following example!
| Method | Endpoint | Description | Success | Failure |
|---|---|---|---|---|
GET |
/api/contacts |
Return all contacts | 200 OK |
400 Bad Request, 404 Not Found |
POST |
/api/contacts |
Add a new contact | 201 Created |
400 Bad Request |
PUT |
/api/contacts/{id} |
Update a contact | 204 No Content |
400 Bad Request, 404 Not Found |
PATCH |
/api/contacts/{id} |
Partially update a contact | 204 No Content |
400 Bad Request, 404 Not Found |
DELETE |
/api/contacts/{id} |
Remove a contact | 200 OK |
404 Not Found |