Creating a context
- Create a context that inherits from
DbContext- Commonly located in the
Modelsfolder, but ideally should be in a separate abstraction/repository folder (for exampleRepositories)
- Commonly located in the
- The class needs to have a constructor that calls the base constructor with
: base(options) - Create a
DbSetproperty for each resourcepublic class ContactsContext : DbContext { public DbSet<Contact> Contacts { get; set; } public ContactsContext(DbContextOptions<ContactsContext> options) : base(options) { } }
- To further configure how the database will be structured, override the
OnModelCreatingmethod - In this example, one table named
Contactwith columnsId,NameandEmailwill be created:public class ContactsContext : DbContext { public DbSet<Contact> Contacts { get; set; } public ContactsContext(DbContextOptions<ContactsContext> options) : base(options) { } protected override void OnModelCreating(ModelBuilder modelBuilder) { modelBuilder.Entity<Contact>().ToTable("Contact"); } }
- In this example, the Contact table will be created with some starting values for
Id,NameandEmailcolumns:public class ContactsContext : DbContext { public DbSet<Contact> Contacts { get; set; } public ContactsContext(DbContextOptions<ContactsContext> options) : base(options) { } protected override void OnModelCreating(ModelBuilder modelBuilder) { modelBuilder.Entity<Contact>().HasData( new Contact { Id = 1, Name = "Johannes Kantola", Email = "johkant@example.com" }, new Contact { Id = 2, Name = "Rene Orosz", Email = "rene_king@example.com" } ); } }
DbContext as a Service
- In
Program.cs, add the context to services withAddDbContextmethod - This is where you set the DB management system you want to use (MySQL, PostgreSQL, SQLite...)
- The EFCore support for PostgreSQL is called
Npgsqlas in the package name
- The EFCore support for PostgreSQL is called
- Add the server, host, port, username, password and the database name of the existing database inside
options.UseNpgsqlas a connection string:services.AddDbContext<ContactsContext>(options => options.UseNpgsql( @"Server=PostgreSQL 12;Host=localhost;Port=5432;Username=postgres;Password=1234;Database=contacts")); services.AddScoped<IContactRepository, ContactRepository>(); services.AddControllers().AddNewtonsoftJson();
Migrations
- As the development progresses, models and database schemas change over time
- This means that both the database and the code needs to be updated to match each other
- Migrations allow for the database to keep in sync with the code schematically
- The data stored in the database is also preserved
- EFCore migrations have built-in version control; a snapshot of each version of the schema is stored
Applying migrations
- Open the Package Manager Console in Visual Studio
- If the tab is not in the bottom of the window, open it from
View > Other windows > Package Manager Console
- If the tab is not in the bottom of the window, open it from
- Add your initial migration by entering the command
Add-Migration <name>to the console, for example
Add-Migration InitialMigration- This now creates the first "blueprint" of how the database should be structured
- Update the database by entering the command
Update-Databaseto the console- This will update the existing database according to the
ModelBuilderoptions
- This will update the existing database according to the
- At this point, the values you have entered (
Contactstable in this example) should show up in the database. You can check it up e.g. in pgAdmin.
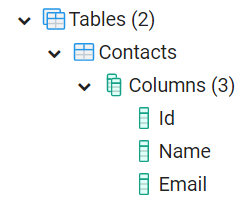
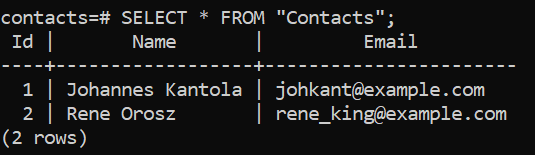
- Notice that the table and column names are initialized with a capital letter
- The value naming in psql is case sensitive
- The value naming in psql is case sensitive
Exercise 1: Adding Context
Continue working on the CourseAPI.
- Create a new empty database
course_dbin pgAdmin or psql - Create a
DbContextfor the courses. Name itCoursesContext, and add aDbSetof typeCourseto it, namedCourses - Add the
OnModelCreatingmethod to the context and add a couple of courses with some starting values to themodelBuilder - Add the
CoursesContextto the services inProgram.cswith a connection string pointing tocourse_db - Add the first migration and update the database from the Package Manager Console
- Check that the
Coursetable with the starting values has appeared to the database
Using DbContext in the API
- Because
DbContextis added to services, it can be accessed from any other service, such as the repository - Using the
DbSetfor each model in your project, CRUD operations can be applied to the database from the repository with LINQ andDbSetmethodsAdd()Update()Remove()
- After modifying the
DbSet, update the changes to the database with theDbContext.SaveChanges()method
Injecting DbContext
- Inject the
DbContextto your repositories as you would any other service:public class ContactRepository : IContactRepository { private readonly ContactsContext _context; public ContactRepository(ContactsContext context) { _context = context; } //... }
DbContext: Read Operations
public class ContactRepository : IContactRepository
{
private readonly ContactsContext _context;
public ContactRepository(ContactsContext context) { ... }
public Contact GetContact(int id) =>
_context.Contacts.FirstOrDefault(c => c.Id == id);
public List<Contact> GetContacts() =>
_context.Contacts.ToList();
}
DbContext: Create Operations
public class ContactRepository : IContactRepository
{
private readonly ContactsContext _context;
public ContactRepository(ContactsContext context) { ... }
// Read operations
// ...
public void AddContact(Contact contact)
{
_context.Contacts.Add(contact);
_context.SaveChanges();
}
}
DbContext: Update Operations
public class ContactRepository : IContactRepository
{
private readonly ContactsContext _context;
public ContactRepository(ContactsContext context) { ... }
// Read & create operations
// ...
public void UpdateContact(int id, Contact newContact)
{
var contact = GetContact(id);
contact.Email = newContact.Email;
contact.Name = newContact.Name;
_context.Contacts.Update(contact);
_context.SaveChanges();
}
}
DbContext: Delete Operations
public class ContactRepository : IContactRepository
{
private readonly ContactsContext _context;
public ContactRepository(ContactsContext context) { ... }
// Read, create & update operations
// ...
public void DeleteContact(int id)
{
_context.Contacts.Remove(GetContact(id));
_context.SaveChanges();
}
}
Exercise 2: CRUD on the DB
Continue working on CourseAPI.
- Modify the
CourseRepositoryto create, read, update and delete from the database instead of the locally stored list of courses - Test with Postman. Keep refreshing the DB in pgAdmin or creating queries with psql to make sure the requests work as intended
Summing Things Up
- Now the API has been hooked up to a PostgreSQL database
- Changes to the schema are kept up-to-date with migrations
- Repository is processing CRUD operations to the database
- Controllers accepting HTTP requests have access to the repository
EFCore Code First Checklist
- Install required packages
- Create
DbContextfor the database - Add
DbContextto services Add-Migration&Update-Database- Add CRUD operations to the database repository
Modifying the Relations
- Let's change the structure of our Contacts API by adding a new class
Account- Instead of
Contactdirectly having anEmail, it will have anAccountinstead Accountholds the information about theEmail, as well as aDescriptionabout the nature of the account (personal, work, school etc.)
- Instead of
- Emails will be removed from the
Contactstable
// Models/Contact.cs
public class Contact
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public ICollection<Account> Accounts { get; set; }
}
// Models/Account.cs
public class Account
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Email { get; set; }
public string Description { get; set; }
public int ContactId { get; set; }
public Contact Contact { get; set; }
}
- Adding a migration at this point will result in a warning:
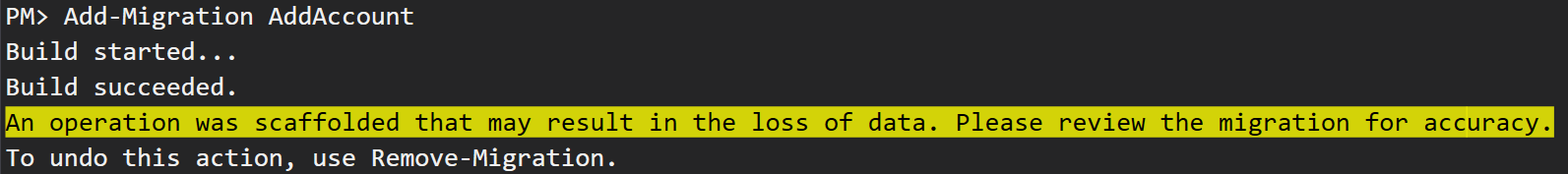
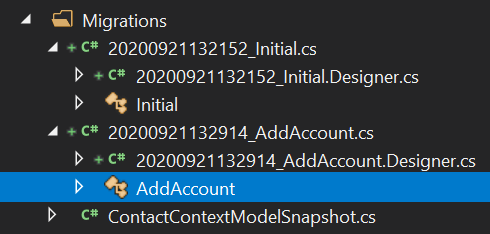
- In the generated migration file, you can find
UpandDownmethods- The
Upmethod describes the changes that will be made with the migration- In this case, removing the
Emailcolumn fromContactstable, and creating the newAccountstable
- In this case, removing the
- The
Downmethod describes the changes that will be made if the migration is reverted
- The
- Updating the database will still work, and the database will have a new table
Accounts
Exercise 3: Adding Migrations
Continue working on CourseAPI.
- Add a new model
Lecturewith propertiesint Id,DateTime StartTime,int Length,Course Course, andint CourseId - Add a new property
ICollection<Lecture> Lecturesto theCoursemodel - Add a new migration named
AddLectures - Update the database. Check that the changes show up in the database with pgAdmin
Database First approach
What is the Database First approach?
- This is the other approach for creating a connection between the database and the application
- Databases and tables are created first, then you create an entity data model using the created database
- This approach is preferred for data intense, large applications
- Other advantages include:
- Data model is simple to create
- GUI
- You do not need to write any code to create your database
Scaffolding
- Use the Package Manager Console to "reverse engineer" the code for an existing database
- This is called scaffolding
- Scaffold the database with the following command:
Scaffold-DbContext "Server=PostgreSQL 12;Host=localhost;Port=5432;Username=postgres;Password=1234;Database=sqlpractice" Npgsql.EntityFrameworkCore.PostgreSQL -OutputDir Models - Using the connection string corresponding to your database, this will create all the classes for the entities in the DB as well as the context class
Exercise 4: Database First
Create a new ASP.NET Core web app using the API template.
- Install the required NuGet packages for using EFCore, EFCore Tools and PostgreSQL
a) by using the package manager, or
b) by copying the<PackageReference>lines from the.csprojfile of the previous assignment to this project's.csprojfile - Scaffold the
sqlpracticedatabase created in SQL Databases Exercise 1 to the project by using the Database First approach. If you have not yet created the database in PostgreSQL, it can be found here
Reading: Authentication with roles
- Here's an example how to do a role-based authentication by using JWT tokens
Exercise 5 (Extra): Connection
Continuing the previous exercise,
- Create and connect Postgres database to API and create a second entity with a relation to the first entity.
- Test your solution.