---
* Sometimes you might have custom requirements and the action should, according to the standard, return a bad request if the action does not fit those requirements
* For example, the simplest possible way to validate the format of an email is to check whether it contains the `@` symbol
* Add an error with `AddModelError` if it does not contain the symbol:
```csharp
if (!contact.Email.Contains('@'))
{
ModelState.AddModelError("Description", "The email is not in valid form.");
}
```
* Then check the model state:
```csharp
if (!ModelState.IsValid)
{
return BadRequest(ModelState);
}
```
## Exercise 1: Add validation
Continue working on CourseAPI.
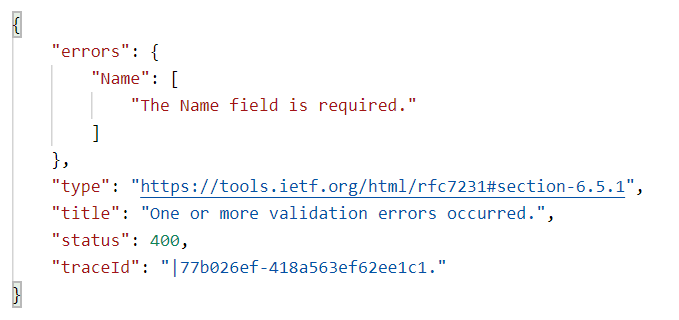
1) Mark all the properties of the Course class with the `[Required]` attribute
2) Create an endpoint for `POST` requests with the URI `api/courses`
3) All the contents of the new course should come from the request body and the new course should be added to the `Courses` list
4) The maximum number of credits should be 20 and minimum 1 (Tip: Use `Range`)
5) Return an appropriate response
## Limiting `PATCH` with validation
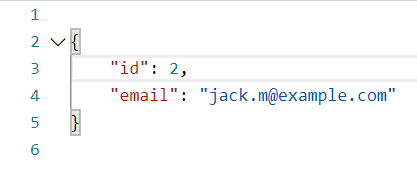
* Suppose we only want to allow the `PATCH` operation to affect `Name` and `Email` properties of the `Contact` class
* Begin by declaring a class with only those fields:
```csharp
// Models/ContactPatch.cs
public class ContactPatch
{
public string Name { get; set; }
public string Email { get; set; }
}
```
---
* Use the `ContactPatch` class instead of the actual class for patching:
```csharp
// Controllers/ContactsController.cs
[HttpPatch("{id}")]
public IActionResult Patch(int id, [FromBody] JsonPatchDocument